NAD⁺: The Fountain of Youth or Just Hype?
Aging is inevitable—but science is increasingly uncovering ways to slow it down at the cellular level, and one molecule continues to stand out: NAD⁺ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide). Touted as a potential “fountain of youth,” NAD⁺ has captured the attention of anti-aging researchers, biohackers, and longevity enthusiasts alike.What is NAD⁺ and Why Does It Matter?
NAD⁺ is a coenzyme found in every living cell, essential for converting nutrients into energy and maintaining cellular function. It plays a central role in:
Metabolic function
DNA repair
Cell signaling
Mitochondrial health
Sirtuin activation (longevity genes)
Unfortunately, NAD⁺ levels decline significantly with age, leading to increased cellular dysfunction and greater vulnerability to age-related diseases.
Studies show that NAD⁺ levels can drop by more than 50% between the ages of 40 and 60.
Medical Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Statements about dietary supplements, including Tru Niagen®, have not been evaluated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Always consult your physician or qualified healthcare provider before beginning any new supplement regimen, especially if you have existing medical conditions, are pregnant or breastfeeding, or are taking prescription medications.
Individual results may vary. Use of this content is at your own risk.
How NAD⁺ Works in the Body
NAD⁺ acts like a cellular battery charger, transferring electrons during metabolic reactions. But its most intriguing role is as a cofactor for sirtuins—a family of proteins linked to longevity, inflammation regulation, and mitochondrial function.
Sirtuins require NAD⁺ to function. When NAD⁺ is depleted, these proteins can't do their job effectively, leading to:
DNA damage
Poor mitochondrial performance
Accelerated cellular aging
Scientific Evidence: What the Research Says
1. Longevity and Cellular Repair
David Sinclair, a Harvard researcher and longevity expert, has extensively studied the connection between NAD⁺ and sirtuins. In a landmark 2013 study, NAD⁺ supplementation in mice rejuvenated mitochondrial function, making older mice appear and function like much younger ones Gomes et al., 2013.
2. Neuroprotection and Cognitive Function
NAD⁺ precursors like NMN and NR (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide and Nicotinamide Riboside) show promise in protecting the brain from age-related decline. A 2018 study published in Cell Reports demonstrated enhanced cognitive function and neurovascular health in aged mice after NMN supplementation Tarantini et al., 2019.
3. DNA Repair and Cancer Resistance
NAD⁺ activates enzymes called PARPs, which play a key role in repairing damaged DNA. As DNA damage accumulates with age, maintaining NAD⁺ levels may help reduce the risk of mutations and certain cancers Belenky et al., 2007.
4. Metabolic Health and Insulin Sensitivity
In clinical trials, Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) improved insulin sensitivity and lowered blood pressure in older adults—suggesting potential benefits for type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular health Martens et al., 2018.
How to Boost NAD⁺ Naturally or Supplementally
Lifestyle Strategies:
Exercise: Aerobic and resistance training both increase NAD⁺ levels naturally.
Fasting and Caloric Restriction: Promote NAD⁺ production by activating sirtuins and autophagy.
Sleep: Quality sleep enhances NAD⁺-dependent metabolic repair mechanisms.
Supplementation:
NR (Nicotinamide Riboside): Marketed under brands like Tru Niagen, shown to be well-tolerated and effective in raising NAD⁺ levels.
NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide): More recently favored for its potential to enter cells more efficiently, with promising preclinical data.
Nicotinamide (NAM): A cheaper option, but may inhibit sirtuins if not carefully balanced.
Note: Consult a healthcare professional before starting NAD⁺ supplements, especially if you have a history of cancer or metabolic disorders.
🧬 Cautions and Limitations
Despite the exciting data, long-term safety and efficacy in humans remain under investigation. Some critics caution against over-supplementation, noting the possibility of:
Increased cell proliferation (including cancer cells)
Disrupted methylation balance
Unknown long-term impacts on the epigenome
More large-scale, peer-reviewed human clinical trials are needed to fully validate NAD⁺ as a longevity therapy.
Is NAD⁺ the Real Fountain of Youth?
While it's no magic pill, NAD⁺ is a key regulator of cellular health and aging. The growing body of research suggests that maintaining optimal NAD⁺ levels may enhance energy, protect against neurodegeneration, and extend healthspan—even if it doesn’t offer immortality.
For now, NAD⁺ represents one of the most promising frontiers in the science of aging, offering tangible steps toward healthier, longer living.
Tru Niagen: What the Research Really Says
Tru Niagen® is a patented form of Nicotinamide Riboside (NR chloride), a precursor to NAD⁺, designed to safely and effectively increase cellular NAD⁺ levels. It is Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) by the FDA and has become one of the most studied and trusted NAD⁺ boosters available to consumers.
1. NAD⁺ Elevation in Humans
One of the most consistently replicated outcomes of Tru Niagen research is its ability to significantly increase NAD⁺ levels in blood and tissues.
Key Study:
Martens et al. (2018) – Nature Communications
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, 60 middle-aged and older adults took 1,000 mg of NR per day for 6 weeks. Results showed:60% increase in NAD⁺ levels from baseline
No serious adverse effects
Improvement in systolic blood pressure in participants with elevated baseline values
Link to study
2. Cardiovascular and Metabolic Health
Tru Niagen has also shown promise in vascular health, particularly in populations with mild hypertension or prediabetes.
Key Study:
Dellinger et al. (2017) – Scientific Reports
A 12-week study showed that NR supplementation led to an increase in NAD⁺ levels and suggested potential benefits to mitochondrial function and inflammatory markers.
Link to study
Martens Follow-Up:
Same 2018 Martens trial also showed a reduction in arterial stiffness and improvement in blood pressure in older adults—key indicators of cardiovascular aging.
3. Brain and Cognitive Support (Emerging Area)
While no large-scale human cognitive trials have been completed, preclinical data on NR show strong neuroprotective potential:
Enhances neurovascular coupling (a fundamental brain process that links neuronal activity to local blood flow — essentially, it ensures that active brain regions get the oxygen and nutrients they need exactly when they need it). This is important because it keeps brain metabolism tightly regulated, ensures efficient delivery of oxygen and glucose, helps remove metabolic waste, supports cognitive performance, memory, learning, maintains blood-brain barrier integrity
Preserves mitochondrial function in brain cells
Reduces age-related inflammation and oxidative stress
Ongoing Trials:
NIH-funded studies are investigating NR’s potential in Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and traumatic brain injury.
4. Cellular Resilience and Aging
NR, via Tru Niagen, activates sirtuins and supports:
DNA repair via PARP activation
How PARP Activation Works
When DNA is damaged (by radiation, toxins, aging, etc.), PARP enzymes "sense" the damage and become activated. Once activated, they:
Use NAD⁺ as fuel to add chains of ADP-ribose (a process called PARylation) to themselves and other proteins.
This attracts and organizes DNA repair proteins to the damaged site.
Once repairs are complete, PARP activity subsides, and normal cellular function resumes.
Improved cellular stress resistance
Maintenance of mitochondrial health
What Is Tru Niagen®?
Tru Niagen contains Nicotinamide Riboside (NR), a unique form of vitamin B3 that:
Is directly converted into NAD⁺
Is bioavailable (absorbed easily)
Has been clinically shown to increase NAD⁺ by up to 60% in as little as 2 weeks
Tru Niagen is patented, third-party tested, and produced by Chromadex, a company deeply involved in NAD⁺ research.
Is Tru Niagen® Safe?
Yes. Across 13+ human clinical trials, Tru Niagen has shown:
Excellent safety profile
Well-tolerated at doses up to 2,000 mg/day
No major adverse effects reported
It is currently FDA GRAS, and approved by Health Canada, the European Commission, and Australia’s TGA. (FDA GRAS stands for "Generally Recognized As Safe" — it’s a designation used by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to indicate that a substance added to food or supplements is considered safe by qualified experts, under the conditions of its intended use).
As early as your 30s, NAD⁺ starts to drop. By age 50+, levels can be cut in half. This affects:
Mental clarity
Sleep quality
Fatigue
Immune resilience
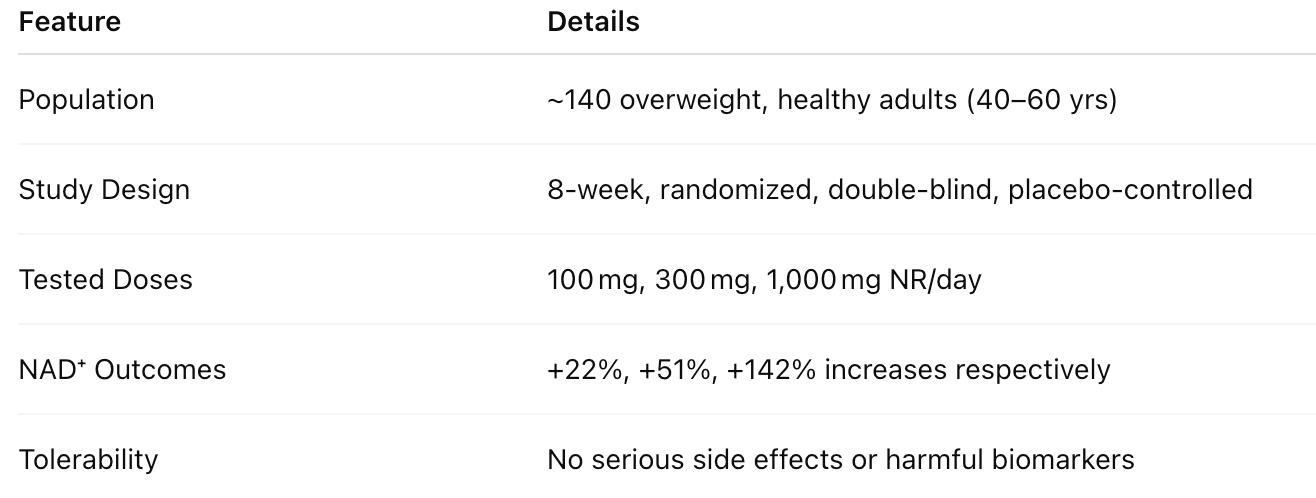
Summary of Key Clinical Trials:
Limitations and What to Watch
Not a cure-all: Tru Niagen enhances NAD⁺, but doesn’t guarantee disease reversal or longevity.
More long-term studies: Needed for conditions like Alzheimer’s, cancer, and immune dysfunction.
Price and accessibility: Premium cost may not be justifiable without clear biomarkers of aging or illness.
Is Tru Niagen Worth It?
Tru Niagen is scientifically validated to raise NAD⁺ levels and support metabolic and cellular health, especially in older adults or those under physiological stress. While more research is needed for disease-specific applications, its safety and biological effectiveness make it a strong candidate in the anti-aging toolkit.
Disclaimer: I am not a representative of Tru Niagen, or in any way affiliated with the company or brand. It is discussed here because of the substantial research, safety, and efficacy.
References
Martens, C. R., et al. (2018). Chronic nicotinamide riboside supplementation is well-tolerated and elevates NAD⁺ in healthy middle-aged and older adults. Nature Communications, 9(1), 1286.
Trammell, S. A. J., et al. (2016). Nicotinamide riboside is uniquely and orally bioavailable in mice and humans. Nature Communications, 7, 12948.
Dellinger, R. W., et al. (2017). Repeat dose NR increases NAD⁺ levels in humans safely. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 40164.
Airhart, S. E., et al. (2017). An open-label, non-randomized study of NR in healthy volunteers. Nature Partner Journals: Aging and Mechanisms of Disease, 3(1), 17.
Gomes, A. P., et al. (2013). Declining NAD⁺ induces a pseudohypoxic state disrupting nuclear-mitochondrial communication during aging. Cell, 155(7), 1624-1638.
Tarantini, S., et al. (2019). Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation rescues neurovascular coupling in aging mice. Cell Reports, 26(4), 934–945.
Belenky, P., et al. (2007). NAD⁺ metabolism in health and disease. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 32(1), 12-19.